-
Global
Global
Aug 29, 2024 View: 1

With the implementation of the two-part tariff policy, enterprises are required to pay both capacity and demand charges. To effectively reduce overall electricity costs, energy storage systems are becoming increasingly important. COSLINK Flexible Commercial and industrial energy storage solution offers an even more effective way to achieve this goal.
Capacity Charges and Demand Charges
For large industrial users with a power consumption of 315 kVA or above, a two-part tariff is typically applied. This tariff model consists of two parts: the energy charge and the basic charge.
1. Energy Charge
This fee is based on the user’s actual electricity consumption and primarily reflects the cost of electricity usage by the enterprise.
2. Basic Charge
This includes capacity charges and demand charges, which are fixed expenses that the enterprise must pay monthly according to a standard rate.
2.1 Capacity Charge
This is based on the maximum capacity of the user’s installed transformer. Even if the user does not fully utilize this capacity, the grid company must reserve sufficient transmission and distribution facilities for potential use, so the need for this charge.
2.2 Demand Charge
This is based on the user's actual maximum power demand. It reflects the user’s peak electricity requirement over a short period, and the grid company needs to ensure it can meet this demand at any time, justifying the demand charge. If the actual demand reaches or exceeds 70% of the transformer capacity, the demand charge is calculated based on 100% of the transformer’s capacity.
How ESS Reduce Enterprise Costs
1. Lowering Actual Energy Costs
Energy storage systems can discharge during peak times and charge during off-peak times, thereby lowering the overall electricity costs for the enterprise. This approach is commonly used in areas with time-of-use pricing.
2. Reducing Basic Charges
By utilizing an energy storage system, enterprises can reduce their reliance on transformers during peak electricity usage. This shifts part of the power demand to the storage system, effectively reducing the transformer’s capacity utilization and dependence on peak-period electricity, which in turn lowers both demand and capacity charges.
3. Providing Backup Power and Minimizing Outage Losses
For commercial and industrial enterprises, power outages or restrictions can result in significant economic losses. Energy storage systems not only serve as backup power but also ensure continuity of production during outages or power limits, preventing additional costs from insufficient power and enabling the enterprise to respond quickly to unexpected outages, minimizing their losses.
Case Analyze
Suppose the demand charge in a certain area is ¥40 per kW per month. An enterprise’s power usage is mostly 800 kW, with some periods reaching 1300 kW.
Without an ESS: The demand charge would be 1300 kW × ¥40/kW·month = ¥52,000/month.
With a 500 kW/1045 kWh COSLINK Active Control ESS Installed: By discharging during peak periods and keeping power demand within 800 kW, the demand charge would be reduced to 800 kW × ¥40/kW·month = ¥32,000/month. Thus, the enterprise could save ¥20,000 in basic charges each month.
According to preliminary estimates, the investment payback period for the ESS is about 5 years. If the system can also participate in other services (such as peak shaving, frequency regulation, virtual grids, etc., with support from a network management platform), the payback period could be further shortened.
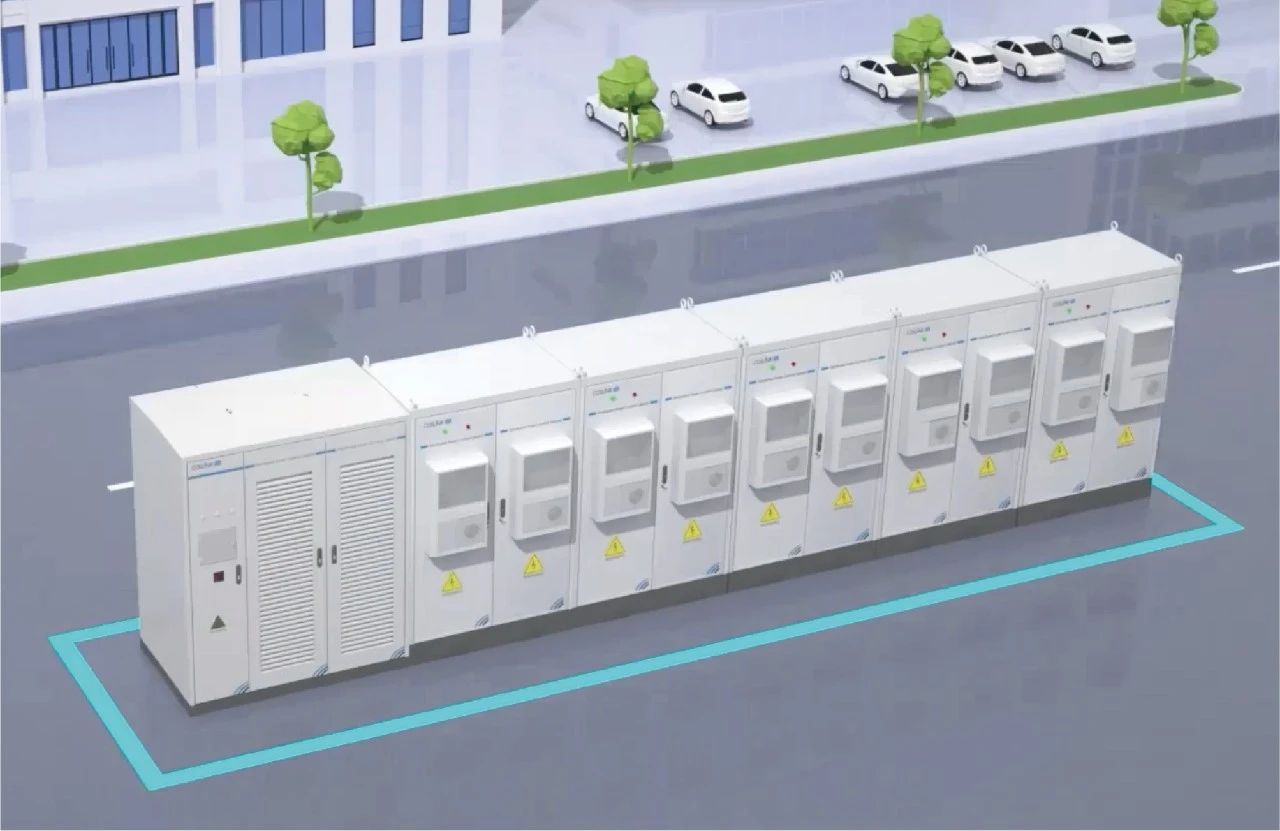
COSLINK Flexible Solution Features
Compared to conventional energy storage systems, COSLINK products have two main features: “flexibility” and “smart control.”
In traditional energy storage solutions, system design must account for the transformer capacity and power load. If the transformer capacity is limited, the storage system’s capacity must be restricted to avoid increasing the enterprise’s demand charges.
In parks with multiple transformers, if one transformer has limited available capacity, the storage capacity for that transformer would be constrained. Conversely, if another transformer has ample remaining capacity but low load, the storage system cannot effectively use it either, as the stored energy may not be discharged promptly. Overall, this significantly limits the total capacity of the storage system.
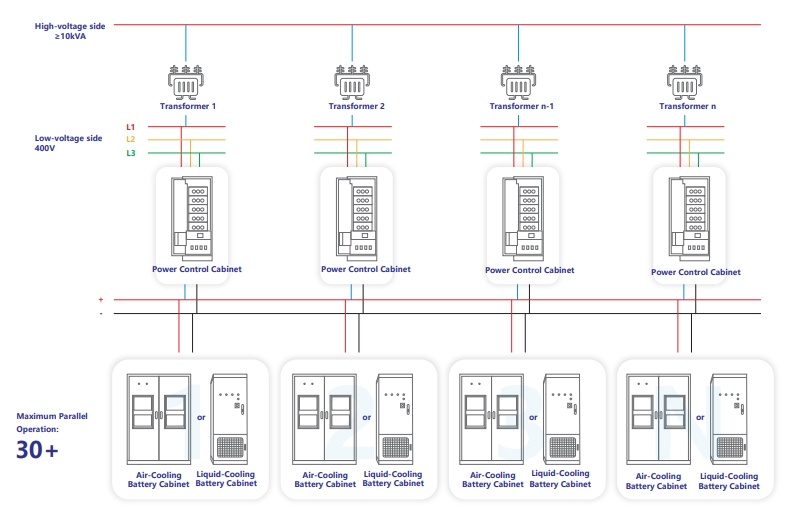
COSLINK solution employs a “multi-port concept”, where all storage cabinets form a unified capacity pool on the low-voltage side. Each storage cabinet is equipped with an active-control optimizer, and and each PCS power controller is integrated with COSLINK exclusive smart control EMS. This allows independent communication and strategy scheduling for each storage cabinet. By adjusting the charging and discharging in real-time based on each transformer's available capacity and load conditions,the system maximizes transformer capacity utilization and minimizes investment costs for the client.
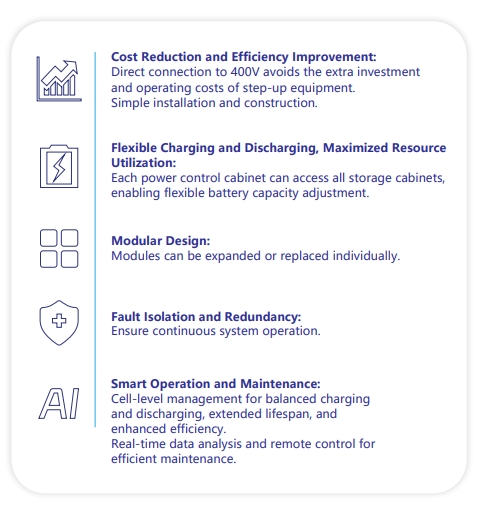
This approach allows for "over-provisioning" of energy storage, significantly enhancing the project’s return on investment and potentially reducing the overall project payback period to 3.5 years. Furthermore, COSLINK smart control EMS and cloud platform can also support future smart grid services, generating additional revenue and further shortening the project’s payback period.

COSLINK Flexible C&I Solution is currently the world's leading distributed energy storage solution for commercial and industry parks, offering unparalleled advantages in both technical routes and product solutions.
For more information about COSLINK flexible solutions, please feel free to contact us!
